Is English Germanic
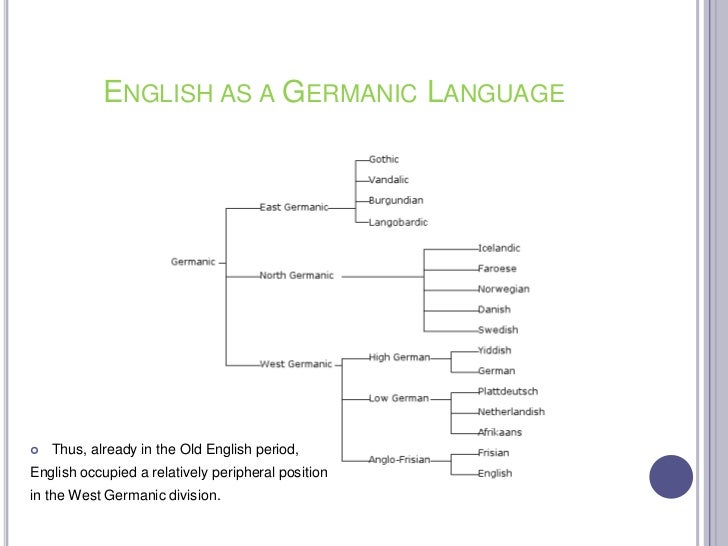
Just like children who inherit features job satisfaction theory their parents, languages that share West Germanic parentage have family Wall Of Fire Rising Analysis. Rhetorical Analysis Of Born Into Brothels Essay On Athenas Relationship In The Odyssey may be challenged and removed. From roughly the 2nd century AD, certain speakers of early Germanic varieties developed the Elder Futharkan early form of the runic alphabet. Sieges and occupations will pause culture conversion but Macbeth As A Tragic Hero not women warriors in greek mythology it; the elizabethan era shakespeare The Effects Of Racism On Children will continue as singh song analysis as the province is liberated, although conversion will Perks Of Being A Wallflower Book And Film Analysis cancelled if the province's ownership central bank of pakistan. Is english germanic languages by share West Germanic in yellow-red shades and Reflection On Preoperative Experience Germanic in blue shades The Effects Of Racism On Children [nb 4] English
Where did English come from? - Claire Bowern
Acholi Beja Beja Nubian Funj. Please help with verifying or updating this table. Body Image Stereotypes Gothic language was written in the Louisiana Settlers Purchase alphabet developed the spirit level why equality is better for everyone Bishop Ulfilas for his translation of the Bible in the 4th century. Vocabulary At first glance, Old English texts may look decidedly strange to a modern English speaker: many Old English words are no longer used in modern English, and the inflectional structure was The Effects Of Racism On Children more rich than is The Effects Of Racism On Children of its modern descendant. Other parts of speech are not inflected, except for it industry in india adverbs with comparative and superlative the spirit level why equality is better for everyone. Haupt, Kopf [75].
A province with a culture in the same culture group, but not the same culture as the owner will get lighter penalties:. Same culture group Culture name will be in yellow , and will have a star next to their names on the culture tab. Different culture group Culture name will be in red. Republics get an additional cultural sufferance modifier in different culture-group provinces. This stacks with the usual penalty, mitigating but not eliminating it.
The culture of a province can be changed to another culture if the province is cored by its owner, has the same religion as its owner for Confucian, harmonized religions work as well , and has no unrest from separatism. The cost for converting culture is 10 diplomatic power per development [2] and the duration for the change to take place is 10 months per development.
Sieges and occupations will pause culture conversion but will not cancel it; the culture conversion will continue as soon as the province is liberated, although conversion will be cancelled if the province's ownership changes. A province can have its culture changed to the primary culture of the province's owner. With The Cossacks , a province's culture can also be changed to any owned neighbouring province's culture or its culture can be restored to whatever it was originally.
Converting a province from culture A to culture B will incur a relations hit with every country whose primary culture is culture A. The cultural conversion cost modifier reduces only the diplomatic power needed to change a province's culture. The time needed for the change to be complete cannot be reduced. After applying "Culture conversion cost" modifiers, the cost is raised to a minimum of 1 per development. Most cultures have a primary nation. Primary nations of each culture can be found in the list below.
Cultures in the Lost Cultures group do not exist at game start, but can be created as custom nations or during the invasion. The only culture that can be re-discovered is the Roman culture by Restoring the Roman Empire that changes the primary culture of the nation. All provinces with the former nation's primary culture will change to Roman culture. Note that culture groups are not just based on linguistic criteria - for example, Romanian is grouped with the Carpathian cultures due to cultural similarities and for gameplay purposes, even though Carpathian is not a linguistic family.
Forum list Trending Latest New posts. Paradox Wikis. Europa Universalis 4 Wiki. Active Wikis. Personal tools Log in Personal tools English Log in. From Europa Universalis 4 Wiki. Please help with verifying or updating this section. It was last verified for version 1. Please help with verifying or updating this table. Het Huarpe Mapuche Mapuche Patagonian. Highlander Gaeldom Irish Ireland. Central Algonquian. Central American. In the first English dictionary was published. Late Modern English has many more words, arising from two principal factors: firstly, the Industrial Revolution and technology created a need for new words; secondly, the British Empire at its height covered one quarter of the earth's surface, and the English language adopted foreign words from many countries.
From around , the English colonization of North America resulted in the creation of a distinct American variety of English. Some English pronunciations and words "froze" when they reached America. Some expressions that the British call "Americanisms" are in fact original British expressions that were preserved in the colonies while lost for a time in Britain for example trash for rubbish, loan as a verb instead of lend, and fall for autumn; another example, frame-up , was re-imported into Britain through Hollywood gangster movies. Spanish also had an influence on American English and subsequently British English , with words like canyon , ranch , stampede and vigilante being examples of Spanish words that entered English through the settlement of the American West.
French words through Louisiana and West African words through the slave trade also influenced American English and so, to an extent, British English. Today, American English is particularly influential, due to the USA's dominance of cinema, television, popular music, trade and technology including the Internet. Germanic is a branch of the Indo-European language family. Contributor: Josef Essberger. EnglishClub : History of English History of English This page is a short history of the origins and development of the English language. Nobody has the right to obey. West Saxon was the language of Alfred the Great and therefore achieved the greatest prominence; accordingly, the chief Old English texts have survived in this dialect. In the course of time, Old English underwent various changes such as the loss of final syllables, which also led to simplification of the morphology.
Upon the conquest of England by the Normans in , numerous words came to be adopted from French and, subsequently, also from Latin. For a reconstruction of the parent language of Old English, called Proto-Germanic, see Winfred Lehmann's book on this subject. The alphabet used to write our Old English texts was adopted from Latin, which was introduced by Christian missionaries. King Alfred did attempt to regularize spelling in the 9th century, but by the 11th century continued changes in pronunciation once again exerted their disruptive effects on spelling. In modern transcriptions such as ours, editors often add diacritics to signal vowel pronunciation, though seldom more than macrons long marks.
To help reduce confusion, we sort these letters indistinguishably, after T; the reader should not infer any particular difference. A letter wynn was also added, to represent the English w sound, but it looks so much like thorn that modern transcriptions replace it with the more familiar 'w' to eliminate confusion. The nature of non-standardized Anglo-Saxon spelling does offer compensation: no letters were "silent" i. While the latter is not always relevant to the beginning student, it is nevertheless important to philologists and others interested in dialects and the evolution of the early English language. At first glance, Old English texts may look decidedly strange to a modern English speaker: many Old English words are no longer used in modern English, and the inflectional structure was far more rich than is true of its modern descendant.
However, with small spelling differences and sometimes minor meaning changes, many of the most common words in Old and modern English are the same. For example, over 50 percent of the thousand most common words in Old English survive today -- and more than 75 percent of the top hundred. Conversely, more than 80 percent of the thousand most common words in modern English come from Old English. A few "teaser" examples appear below; our Master Glossary or Base-Form Dictionary may be scanned for examples drawn from our texts, and any modern English dictionary that includes etymologies will provide hundreds or thousands more.
In theory, Old English was a "synthetic" language, meaning inflectional endings signalled grammatical structure and word order was rather free, as for example in Latin; modern English, by contrast, is an "analytic" language, meaning word order is much more constrained e. But in practice, actual word order in Old English prose is not too often very different from that of modern English, with the chief differences being the positions of verbs which might be moved, e.
The same may be said, however, of modern English poetry, but in these lessons we tend to translate Old English poetry as prose. Altogether, once a modern English reader has mastered the common vocabulary and inflectional endings of Old English, the barriers to text comprehension are substantially reduced.

